Photo courtesy of Pexels
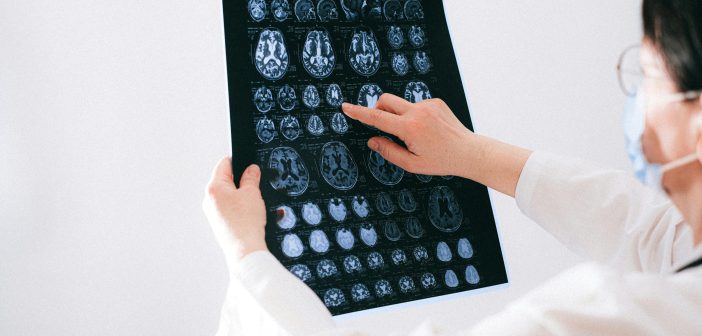
Neurological conditions affect the brain, spinal cord, and nervous system, often leading to significant health challenges. These conditions can arise due to genetic disorders, congenital abnormalities, infections, injuries, and lifestyle influences. While some neurological disorders develop over time, others appear suddenly due to trauma or illness.
According to the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), over one in three people are affected by neurological conditions, making them the leading cause of illness and disability worldwide. Understanding these conditions and recognizing their symptoms can help individuals seek timely medical assistance. In this article, we will review common neurological disorders and their symptoms.
Strokes
Strokes affect over 795,000 people in the U.S. annually. A stroke occurs when the brain’s blood supply is interrupted, either due to a clot or a burst blood vessel. This deprivation of oxygen leads to brain cell damage, potentially causing permanent disability or death. The F.A.S.T. mnemonic helps identify stroke symptoms:
- F: Facial drooping
- A: Arm weakness
- S: Speech difficulties
- T: Time to call emergency services
Strokes can sometimes be mistaken for other conditions, such as seizures or brain tumors, making prompt diagnosis crucial.
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common neurological disorder involving recurrent seizures caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain. Seizures can be triggered by factors such as head injuries, infections, metabolic imbalances, or flashing lights. Symptoms of seizures vary but may include:
- Sudden loss of consciousness or awareness
- Uncontrolled jerking movements of the arms and legs
- Staring spells or temporary confusion
- Rapid eye blinking or rolling of the eyes
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
Proper treatment, including medication and lifestyle adjustments, can help people manage seizures effectively.
Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurological condition and the most common cause of dementia. It primarily affects older adults, with an estimated 6.9 million Americans aged 65 and older living with Alzheimer’s today.
The disease is characterized by the build-up of abnormal proteins in and around brain cells, leading to memory loss, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes. While the exact cause is still unknown, the risk factors include genetics, age, cardiovascular health, and environmental factors such as air pollution. Early symptoms to watch for include difficulty remembering recent events, struggling with familiar tasks, getting lost in familiar places, and noticeable mood or personality changes.
Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a neurological disorder that affects movement, muscle tone, and posture. It is typically caused by brain damage occurring before, during, or shortly after birth. Factors such as premature birth, infections during pregnancy, or lack of oxygen to the brain can contribute to CP. Symptoms of cerebral palsy vary in severity and may include:
- Muscle stiffness or spasticity
- Uncoordinated movements
- Difficulty with balance and posture
- Speech and swallowing difficulties
- Developmental delays in motor skills
While there is no cure, therapy, medication, and assistive devices can help individuals with CP improve their mobility and quality of life.
Recognizing the early symptoms of neurological conditions like strokes, epilepsy, Alzheimer’s, and cerebral palsy can lead to timely medical treatment, which can help individuals manage their symptoms better and improve their overall quality of life.




Guten Tag, ich suche nach einer Firma, die sich auf das Verfassen von wissenschaftlichen Arbeiten, insbesondere Bachelor- und Masterarbeiten, spezialisiert hat. Es wäre hilfreich, wenn diese Firma Erfahrung mit verschiedenen Fachbereichen hat und professionellen Support bei der Erstellung einer wissenschaftlichen Arbeit bieten kann. Dabei interessiert mich sowohl die Qualität der Arbeiten als auch die Einhaltung von Fristen und akademischen Standards. Hat jemand vielleicht eine Empfehlung für eine zuverlässige Firma, die diesen Service anbietet?
Es gibt viele Aspekte, die man bei der Entscheidung berücksichtigen muss, ob man eine Bachelorarbeit selbst schreibt oder einen Ghostwriter https://xn--ghostwriter-sterreich-sec.at/bachelorarbeit-schreiben-lassen/ beauftragt. Ein Thema, das oft in Diskussionen auftaucht, ist, wie viel Unterstützung man von außen holen sollte, um die akademischen Anforderungen zu erfüllen. Viele Studierende in Österreich entscheiden sich dafür, ihre Bachelorarbeit von einem erfahrenen Ghostwriter schreiben zu lassen, um sich den Stress der letzten Wochen vor der Abgabe zu ersparen .
Das Schreiben einer Bachelorarbeit ist zweifellos eine anspruchsvolle Aufgabe. Es erfordert nicht nur fundiertes Wissen, sondern auch die Fähigkeit, dieses Wissen klar und präzise zu formulieren. Die Zeit, die dafür investiert werden muss, kann oft dazu führen, dass Studierende ihre anderen Verpflichtungen vernachlässigen müssen. Eine Lösung, die immer häufiger in Betracht gezogen wird, ist die Unterstützung durch einen Ghostwriter. Ein professioneller Ghostwriter kann nicht nur das Schreiben übernehmen, sondern auch sicherstellen, dass die Arbeit den akademischen Standards entspricht.
Ein Ghostwriter in Österreich kann eine wertvolle Hilfe sein, vor allem für diejenigen, die Schwierigkeiten haben, ihre Gedanken zu Papier zu bringen oder einfach nicht die nötige Zeit haben, sich intensiv mit ihrer Bachelorarbeit auseinanderzusetzen. Ghostwriter sind erfahrene Experten, die sich in der wissenschaftlichen Arbeit bestens auskennen. Sie verstehen, was in einer Bachelorarbeit erwartet wird, und können sicherstellen, dass die Arbeit sowohl inhaltlich als auch formell den Anforderungen entspricht.
Ich danke Ihnen!
When choosing a forum to discuss online casinos, I found this forum – http://www.rollandwin.com/forum/ . and I really liked it, because it is really a very high quality and very cool forum for discussing online casinos! That’s why I recommend it, because it’s very high quality and perfect for discussing casinos!
Experience the thrill of gaming at CruZino Casino! https://crusinocasino.net/ With a wide selection of exciting slots, live games, and exclusive promotions, your chances to win big are just a click away. Enjoy smooth and secure gameplay while earning rewards with every spin. Whether you’re a seasoned player or a beginner, CruZino Casino offers something for everyone. Sign up now and start your journey towards big wins today!
Neurological disorders impact millions worldwide—awareness and early detection can save lives! https://s.w.org/images/core/emoji/15.0.3/svg/1f9e0.svghttps://s.w.org/images/core/emoji/15.0.3/svg/1f499.svg
4o
More and more enterprises are switching to outsourcing to strengthen their positions in a dynamic market and increase cost-efficiency. It is confirmed by Techbehemoths, who surveyed 324 small and medium-sized IT companies. About 77% of respondents admit that they value outsourcing for cost-effectiveness and flexibility.
More https://gloriumtech.com/risks-of-outsourcing/
We provide support for those looking for ‘Take my GED for me’ or ‘Take my TEAS exam’ solutions. Need help with your GED or TEAS exam? We offer services so you can pay someone to take your GED or TEAS exam, hire someone for exam assistance and solutions.
Hire someone To Take My GED exam
Are you looking for who will ‘Write My Dissertation For Me?’ We provide support for those looking for ‘Dissertation Writing Services’ or ‘Dissertation Help’. We offer services so you can ‘Pay Someone To Do Your Dissertation’.
Pay Someone To Do My Dissertation
Neurological conditions like migraines, Parkinson’s disease, and dystonia can impact daily life, requiring proper diagnosis and treatment. Understanding symptoms early helps in effective management and care. Xeomin vs Botox is often compared for treating muscle spasms and wrinkles, with Xeomin offering a purer formula without added proteins.
This is a very informative overview of some of the most impactful neurological disorders. Raising awareness about early symptoms and causes is essential for timely diagnosis and care.
Interestingly, AI Consulting Services are beginning to play a role in healthcare innovation, especially in neurology. AI can assist in early diagnosis of conditions like Alzheimer’s by analyzing MRI scans or tracking cognitive patterns over time. Similarly, machine learning models are being used to predict stroke risks based on patient data. It’s amazing to see how technology and healthcare are merging to improve lives!
today you give me new thoughts, I learned something new.